Scanning repositories
Learn how to scan GitHub repositories to detect AI/ML usage across code, workflows, and infrastructure.
Overview
AI Detection scans GitHub repositories to identify AI and machine learning libraries in your codebase. It helps organizations discover "shadow AI" — AI usage that may not be formally documented or approved — and supports compliance efforts by maintaining an inventory of AI technologies.
The scanner analyzes source files, dependency manifests, CI/CD workflows, container definitions, and model files to detect over 80 AI/ML frameworks and infrastructure patterns including OpenAI, TensorFlow, PyTorch, LangChain, and more. Results are stored for audit purposes and can be reviewed at any time from the scan results.
Starting a scan
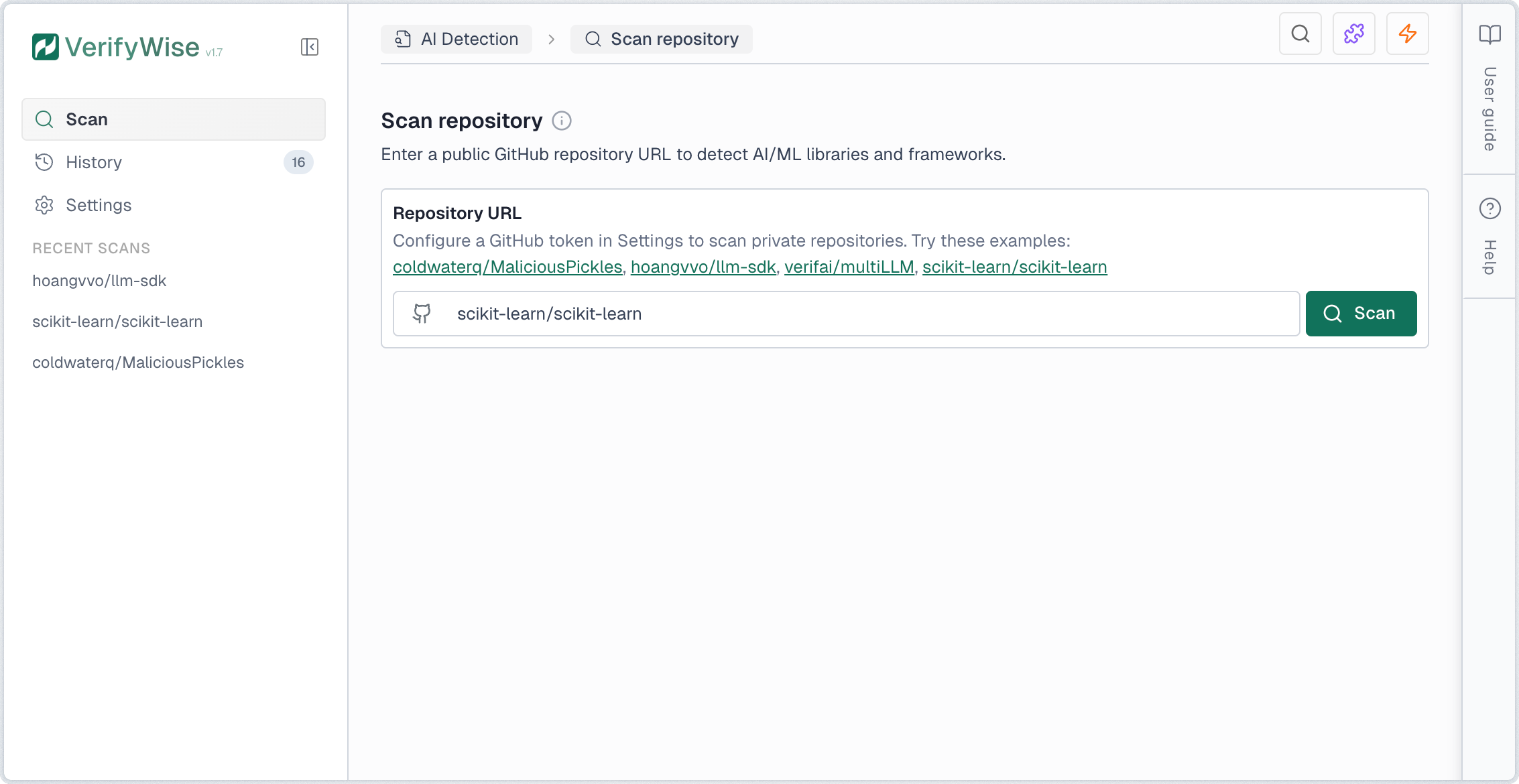
To scan a repository, enter the GitHub URL in the input field. You can use either the full URL format (https://github.com/owner/repo) or the short format (owner/repo). Click Scan to begin the analysis.
Scan progress
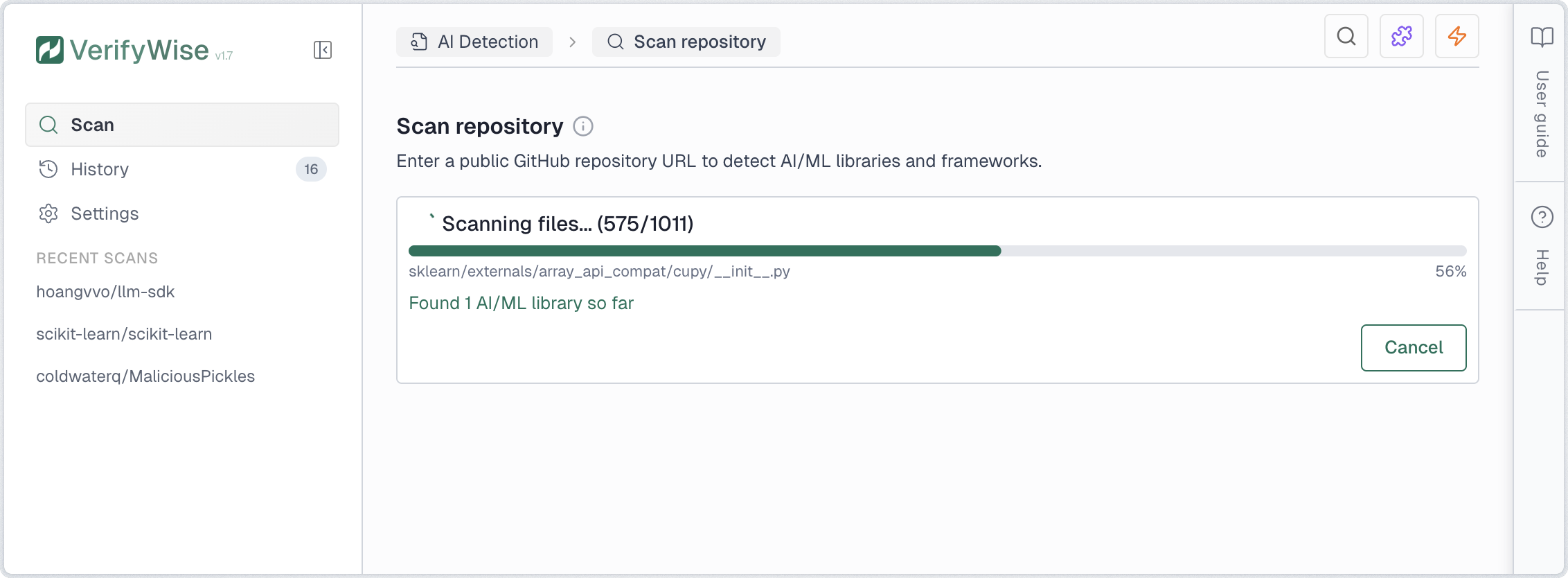
Once initiated, the scan proceeds through several stages. A progress indicator shows real-time status including the current file being analyzed, total files processed, and findings discovered.
- Cloning: Downloads the repository to a temporary cache
- Scanning: Analyzes files for AI/ML patterns and security issues
- Completed: Results are ready for review
You can cancel an in-progress scan at any time by clicking Cancel. The partial results are discarded and the scan is marked as cancelled in the history.
Statistics dashboard
The scan page displays key statistics about your AI Detection activity. These cards provide a quick overview of your scanning efforts and findings.
- Total scans: Number of scans performed, with a count of completed scans
- Repositories: Unique repositories that have been scanned
- Total findings: Combined count of all AI/ML detections across all scans
- Libraries: AI/ML library imports and dependencies detected
- API calls: Direct API calls to AI providers (OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.)
- Security issues: Hardcoded secrets and model file vulnerabilities combined
Understanding results
Scan results are organized into eight tabs covering different aspects of AI/ML usage in your codebase:
- Libraries: Detected AI/ML frameworks and packages
- API calls: Direct integrations with AI provider APIs
- Models: References to AI/ML model files and pre-trained models
- RAG: Retrieval-Augmented Generation components and vector databases
- Agents: AI agent frameworks and autonomous system components
- Secrets: Hardcoded API keys and credentials
- Security: Model file vulnerabilities and security issues
- Compliance: EU AI Act compliance mapping and checklist
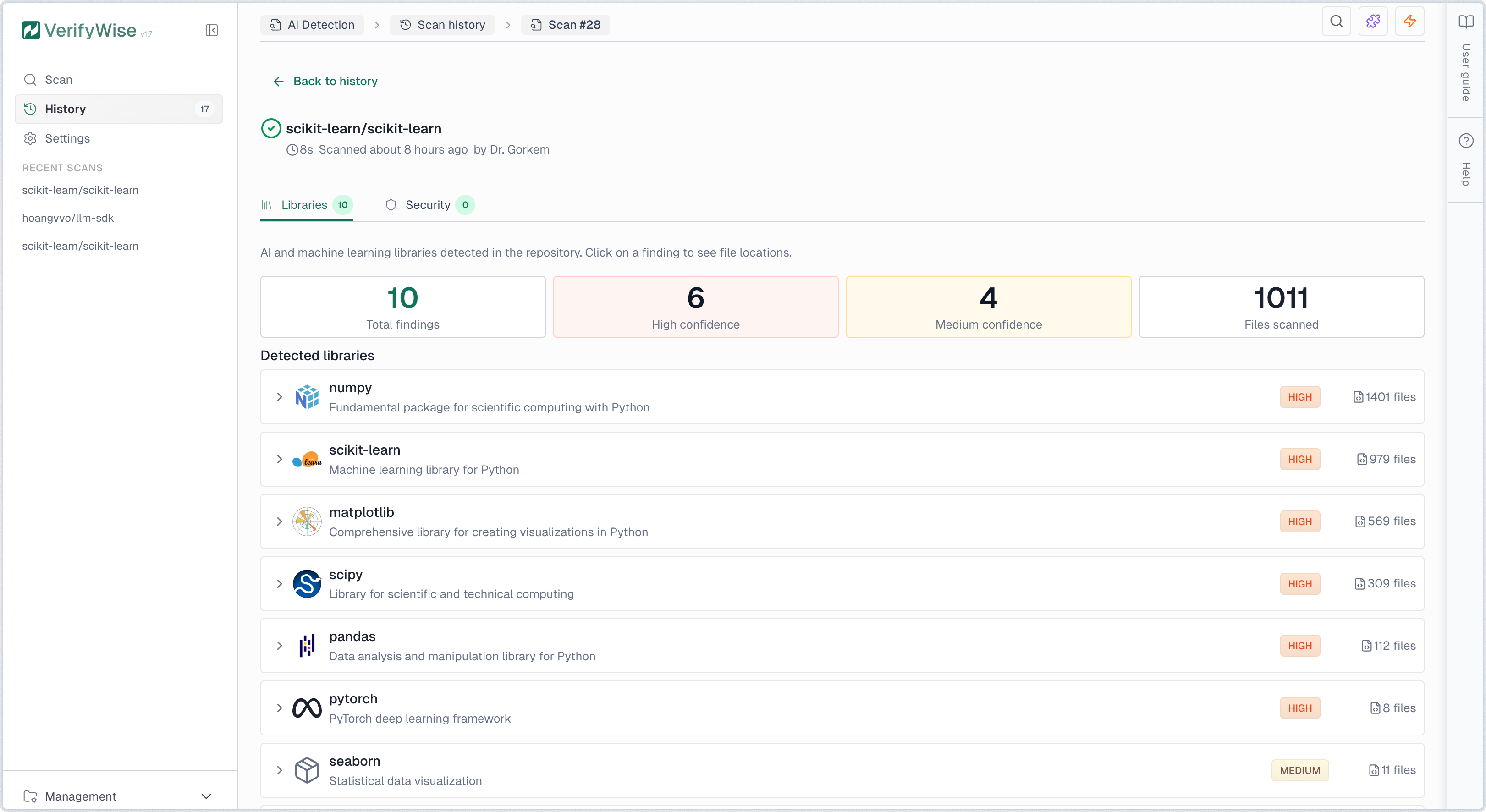
Libraries tab
The Libraries tab displays all detected AI/ML technologies. Each finding shows the library name, provider, risk level, confidence level, and number of files where it was found. Click any row to expand and view specific file paths and line numbers. Detection covers source code imports, dependency manifests, Dockerfiles, and docker-compose configurations.
Risk levels indicate the potential data exposure:
- High risk: Data sent to external cloud APIs. Risk of data leakage, vendor lock-in, and compliance violations.
- Medium risk: Framework that can connect to cloud APIs depending on configuration. Review usage to assess actual risk.
- Low risk: Local processing only. Data stays on your infrastructure with minimal external exposure.
Confidence levels indicate detection certainty:
- High: Direct, unambiguous match such as explicit imports or dependency declarations
- Medium: Likely match with some ambiguity, such as generic utility imports
- Low: Possible match requiring manual verification
Governance status
Each library finding can be assigned a governance status to track review progress. Click the status icon on any finding row to set or change its status:
- Reviewed: Finding has been examined but no decision made yet
- Approved: Usage is authorized and compliant with organization policies
- Flagged: Requires attention or is not approved for use
API Calls tab
The API Calls tab shows direct integrations with AI provider APIs detected in your codebase. These represent active usage of AI models and services, such as calls to OpenAI, Anthropic, Google AI, and other providers.
API call findings include:
- REST API endpoints: Direct HTTP calls to AI provider APIs (e.g., api.openai.com)
- SDK method calls: Usage of official SDKs (e.g., openai.chat.completions.create() or client.chat.completions.create())
- Framework integrations: LangChain, LlamaIndex, and other framework API calls
- CI/CD pipeline usage: AI service secrets referenced in GitHub Actions workflows (e.g., ${{ secrets.OPENAI_API_KEY }})
Secrets tab
The Secrets tab identifies hardcoded API keys and credentials in your codebase. These should be moved to environment variables or a secrets manager to prevent accidental exposure.
The scanner detects common AI provider API key patterns:
- OpenAI API keys: Keys starting with sk-...
- Anthropic API keys: Keys starting with sk-ant-...
- Google AI API keys: Keys starting with AIza...
- Other provider keys: AWS, Azure, Cohere, and other AI service credentials
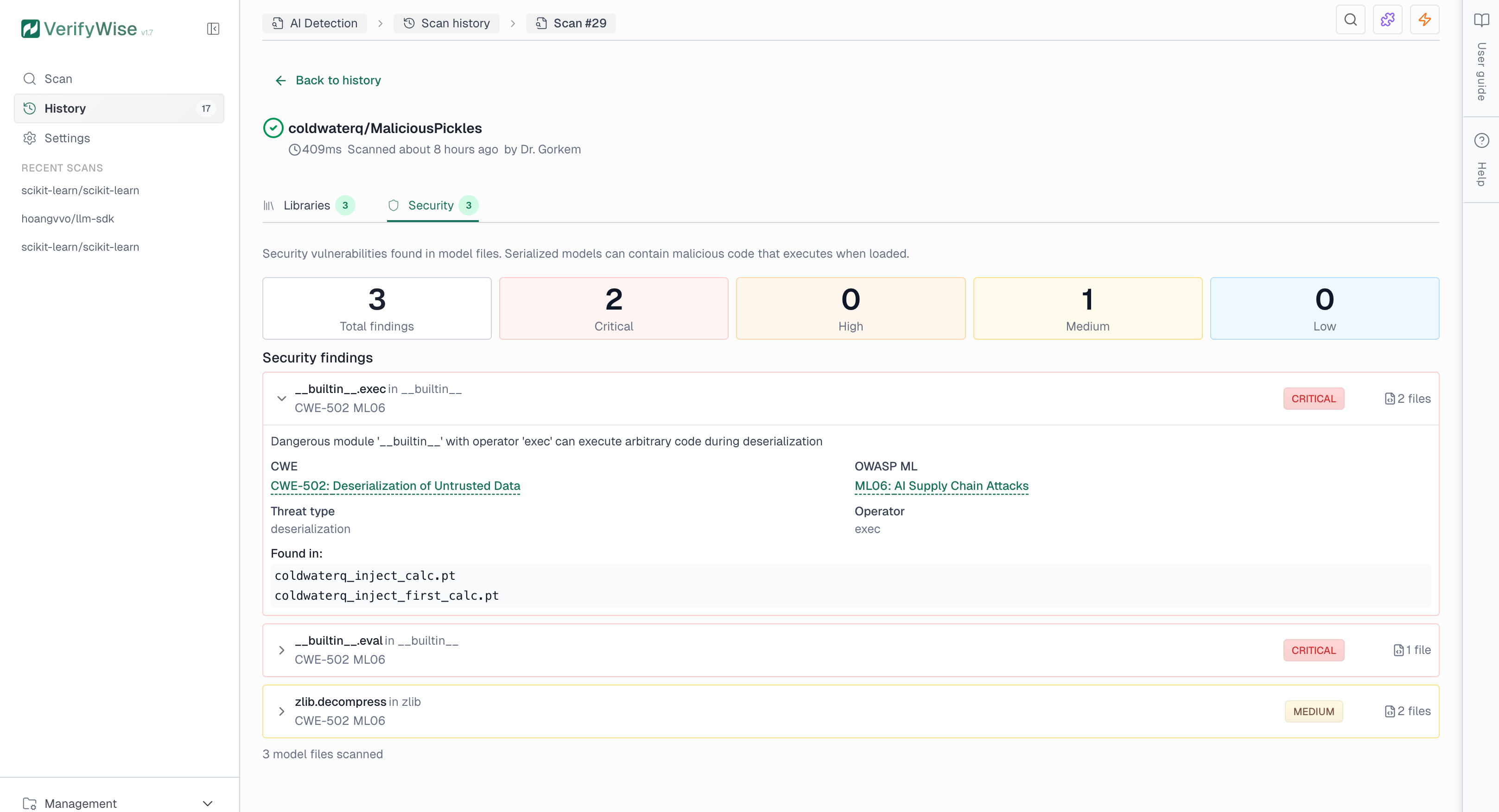
Security tab
The Security tab shows findings from model file analysis. Serialized model files (.pkl, .pt, .h5) can contain malicious code that executes when loaded. The scanner detects dangerous patterns such as system command execution, network access, and code injection.
Security findings include severity levels and compliance references:
- Critical: Direct code execution risk — immediate investigation required
- High: Indirect execution or data exfiltration risk
- Medium: Potentially dangerous depending on context
- Low: Informational or minimal risk
Models tab
The Models tab displays references to AI/ML model files detected in your codebase. This includes pre-trained models, model checkpoints, and model loading patterns.
- Pre-trained models: References to Hugging Face models, OpenAI models, and other hosted models
- Local model files: Model weights stored in the repository (.pt, .h5, .onnx, etc.)
- Model loading code: Code that loads or initializes ML models
RAG tab
The RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) tab identifies components used for building RAG systems. These systems combine retrieval mechanisms with generative AI models.
- Vector databases: Integrations with Pinecone, Qdrant, Chroma, Weaviate, and other vector stores
- Embedding models: Code that generates embeddings for documents or queries
- Retrieval pipelines: LangChain retrievers, LlamaIndex query engines, and similar patterns
Agents tab
The Agents tab shows AI agent frameworks and autonomous system components. AI agents can execute multi-step tasks, use tools, and make decisions independently.
- Agent frameworks: LangChain agents, CrewAI (including @agent and @crew decorators), AutoGen, Swarm, and similar frameworks
- MCP servers: Model Context Protocol server implementations and configuration files (mcp.json, claude_desktop_config.json)
- Tool usage: Code that defines or uses tools for AI agents
- Planning components: Task planning and execution orchestration code
Compliance tab
The Compliance tab maps your scan findings to EU AI Act requirements and generates a compliance checklist. This helps identify regulatory obligations based on the AI technologies detected in your codebase.
The compliance mapping covers key requirement categories:
- Transparency: Requirements for disclosing AI system usage and capabilities
- Data governance: Requirements for data quality, bias prevention, and privacy
- Documentation: Technical documentation and record-keeping obligations
- Human oversight: Requirements for human supervision of AI systems
- Security: Cybersecurity and resilience requirements
Infrastructure and CI/CD detection
Beyond source code, the scanner also detects AI usage in infrastructure and CI/CD configuration files. This helps surface AI technologies that may not appear in application code but are present in deployment pipelines and container definitions.
GitHub Actions workflows
YAML workflow files (.yml, .yaml) are scanned for references to AI services. The scanner detects GitHub Actions that use AI provider actions and secrets references such as OPENAI_API_KEY, ANTHROPIC_API_KEY, and similar tokens in workflow environment variables.
Docker and container images
Dockerfiles and docker-compose files are scanned for AI/ML container images. Detected images include:
- GPU compute: NVIDIA CUDA and NGC container images
- ML frameworks: PyTorch, TensorFlow, and Hugging Face container images
- Inference servers: Ollama, vLLM, and NVIDIA Triton Inference Server
- ML operations: MLflow tracking and serving containers
MCP server configuration
The scanner detects Model Context Protocol (MCP) configuration files such as mcp.json and claude_desktop_config.json. These files define MCP servers that extend AI assistants with external tools and data sources, and are flagged as agent-type findings.
Export and visualization
Completed scans offer several features for analysis and reporting:
- Risk scoring: Calculate an AI Governance Risk Score (AGRS) that evaluates findings across five risk dimensions. Optionally enable LLM-enhanced analysis for narrative summaries, recommendations, and suggested risks that can be added to your risk register.
- View graph: Opens an interactive dependency graph showing relationships between AI components. Nodes represent findings and edges show inferred dependencies based on shared files and providers.
- Export AI-BOM: Downloads the scan results as an AI Bill of Materials (AI-BOM) in JSON format. The AI-BOM follows a CycloneDX-inspired structure and includes all detected components, their providers, risk levels, and file locations.
Compliance references
Security findings include industry-standard references to help with compliance reporting:
- CWE: Common Weakness Enumeration — industry standard for software security weaknesses (e.g., CWE-502 for deserialization vulnerabilities)
- OWASP ML Top 10: OWASP Machine Learning Security Top 10 — identifies critical security risks in ML systems (e.g., ML06 for AI Supply Chain Attacks)
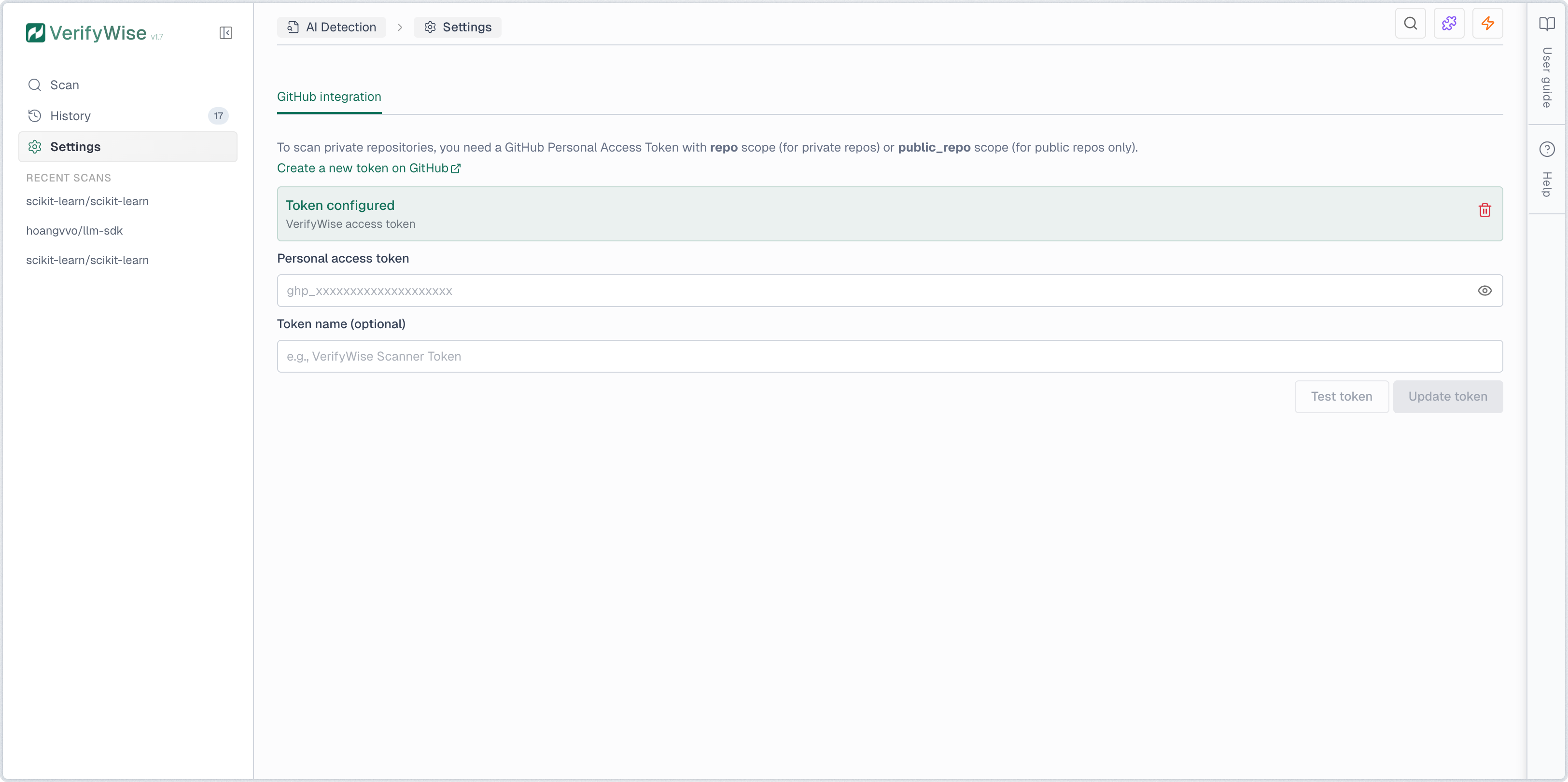
Scanning private repositories
To scan private repositories, you must configure a GitHub Personal Access Token (PAT) with the repo scope. Navigate to AI Detection → Settings to add your token. The token is encrypted at rest and used only for git clone operations.
For instructions on creating a GitHub PAT, see the official GitHub documentation at https://docs.github.com/en/authentication/keeping-your-account-and-data-secure/creating-a-personal-access-token.